Fioricet is also called Acetaminophen (APAP), Butalbital, and Caffeine.
What Is Fioricet?
Fioricet is a combination medication consisting of butalbital, acetaminophen, and caffeine. This medication is generally prescribed to treat tension headaches or migraines. Because Fioricet is a mixture of different drugs, they all work together to relieve headache pain and discomfort. Butalbital is a barbiturate, or sedative, that is effective for decreasing anxiety and causing relaxation and sleepiness. Acetaminophen works to reduce the pain for a headache and caffeine works to increase the effects of acetaminophen.
Fioricet is available in capsule and tablet form and is directed to be taken orally by mouth. The medication is prescribed with caution because of butalbital, which is habit-forming and has the potential for abuse. As a barbiturate, butalbital is addictive and may lead to physical dependence. When abused, Fioricet may lead to addiction.
Fioricet abuse occurs when the drug is taken in ways other than directed, in large amounts, or without a prescription. The butalbital found in Fioricet may produce a high, or feelings of euphoria and intoxication. After prolonged Fioricet abuse, a person is lik
Acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine, are used together in an oral preparation to treat pain, specifically headaches. Acetaminophen is a non-narcotic analgesic for pain and headache relief. Butalbital is a barbiturate used for its sedative effects. Caffeine is found in many analgesic formulations and may be beneficial in Migraine and vascular headaches.
Fioricet is also available with codeine. The combination of acetaminophen and codeine produces a greater analgesic effect than that produced by acetaminophen alone or by higher doses of opiate. Also, this combination might cause fewer adverse reactions than do equianalgesic doses of either agent alone.
Fioricet with Codeine is controlled medicine. Please do not buy fioricet with Codeine online because it is illegal.
Fioricet is a prescription medication used to relieve tension headaches. It works by relaxing muscle contractions that can result in mild to moderate head pain.
Fioricet is a combination of three ingredients: the pain reliever acetaminophen; butalbital, a barbiturate; and caffeine, a stimulant.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Fioricet in 1984. Novartis Pharmaceuticals was the original manufacturer. In 2003, Watson Pharmaceuticals bought the rights to Fioricet (Watson is now known as Actavis).
Fioricet is currently available from many manufacturers as a generic.
The original formulation of Fioricet included 50 milligrams (mg) of butalbital, 40 mg of caffeine, and 325 mg of acetaminophen.
However, in 2011 the FDA asked makers of prescription combination drugs with acetaminophen to limit the amount of that drug to no more than 325 mg in each tablet by 2014. This action was taken to protect consumers from severe liver damage, a risk linked with taking too much acetaminophen.
Today Fioricet includes 320 mg of acetaminophen, though some versions of the product sold online still have 325 mg.
Proper Use of Acetaminophen/butalbital/caffeine
- Take Acetaminophen/butalbital/caffeine exactly as directed by your doctor. If you do not understand these directions, ask your pharmacist, nurse, or doctor to explain them to you.
- Take each dose with a full glass of water.
- Take Acetaminophen/butalbital/caffeine with food or milk if it upsets your stomach.
- Never take more of this medication than is prescribed for you. Too much Acetaminophen/butalbital/caffeine could be very harmful. Never take more than six tablets or capsules per day.
- Do not share this medication with anyone else.
- Avoid alcohol. Alcohol taken during therapy with acetaminophen and butalbital can be very damaging to your liver and can increase drowsiness and dizziness.
- This medicine will relieve a head pain best if you take it as soon as the pain begins. If you get warning signs of a migraine, take this medicine as soon as you are sure that the migraine is coming. This may even stop the head pain from occurring. Lying down in a quiet, dark room for a while after taking the medicine also helps to relieve head pain.
- People who who have frequent head pain episodes may need to take a different medicine to help prevent headaches or Migraines. It is important that you follow your doctor’s directions about taking the other medicine, even if your headaches or Migraines continue to occur. Preventive medicines may take several weeks to start working. Even after they do start working, your headaches or Migraines may not go away completely. However, they should occur less often, and should be less severe and easier to relieve than before.
Fioricet (Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine) Dosage
The recommended dose:
-
-
- 1 to 2 capsules every 4 hours as you need it for pain
- Do not take more than 6 capsules daily.
-
You should not use Fioricet long term, due to the possibility for physical dependence and abuse.
Missed Dose of Fioricet
If you miss a scheduled dose, take it when you remember it. However, if it is nearly time for the next dose, just resume your regular medication schedule. Never double up on doses.

Fioricet Side Effects
Butalbital-containing medications such as Fioricet (butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine) and Fiorinal (butalbital/aspirin/caffeine) have long been implicated in the development of rebound (medication overuse) headaches. One of the problems with Fioricet is that it has a long half-life of about 36 hours, which means that it takes 1.5 days for the body to eliminate half of the dose of the drug. It takes between 5 to 6 half-lives for the drug to reach a steady state, and you can still see traces of the drug in the blood and urine for more than 10 days after taking Fioricet or Fiorinal.
There is an increased risk of tolerance and habituation to the drug when taking multiple doses daily. Weaning off the drug is usually done slowly since there is a risk of seizures and/or delirium. The severity of withdrawal symptoms is directly related to the amount of the medication taken and can include anxiety, weakness, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, involuntary muscle twitching, fatigue, decreased blood pressure, and dizziness.
Withdrawal symptoms can be seen within 8 to 36 hours after the last dose is taken. A recent recommendation from the American Academy of Neurology has stated, “Don’t use opioid or butalbital treatment for migraine except as a last resort.” (Langer -Gould AM, Anderson WE, Armstrong MJ, et al. The American Academy of Neurology’s TOP Five Choosing Wisely recommendations. Neurology. 2013;81:1004-1011.)
Regarding alternatives in the treatment of migraine, the most important is the use of daily preventive medication(s) for long-term migraine control. This can include a single daily preventive medication or a combination of medications. Commonly prescribed daily preventive medications include beta blockers, antiepileptic medications, or tricyclic antidepressants.
OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) is FDA-approved for the prevention of chronic migraine and can be an effective option in some patients. Last year, the FDA approved a device, Cefaly, which delivers microimpulses in order to stimulate nerve endings in the trigeminal nerve and may help to decrease migraine frequency. Treatment of migraine with acute medications such as triptans, ergotamine, or anti-inflammatory agents should be limited to no more than 2 to 3 days per week in order to prevent the development of rebound headache.
The most common side effects from Fioricet include:
-
-
- Drowsiness
- Upset stomach
- Vomiting
- Stomach pain
- Depression
- Lightheadedness
- Confusion
-
The following side effects could be signs of allergy or more serious complications and should be reported to health provider immediately:
-
-
- Skin rash
- Itching
- Difficulty breathing
-
This is not an exhaustive list of all potential side effects of Fioricet. For more information, consult your doctor or healthcare provider. If you notice any new or worsening side effects, contact your doctor or healthcare provider immediately.
Is Fioricet Controlled Substance ?
According to the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), Fioricet is not a controlled substance. However, butalbital belongs to a class of drugs known as barbiturates. These drugs are habit-forming and can be abused. For this reason, it’s not recommended to take Fioricet long-term.
Butalbital affects the central nervous system and can make you sleepy. It can also cause lightheadedness, dizziness and mental confusion. Drowsiness is also one of the first signs of an overdose from barbiturates.
How much caffeine is in Fioricet ?
Fioricet contains 40 mg of caffeine, similar to a cup of tea. The following shows the average amount of caffeine in some common beverages:
-
- 8 oz of coffee: 80 to 100 mg of caffeine
- 8 oz green or black tea: 30 to 50 mg of caffeine
- 12 oz caffeinated soda: 30 to 40 mg of caffeine
How Does Fioricet Work?
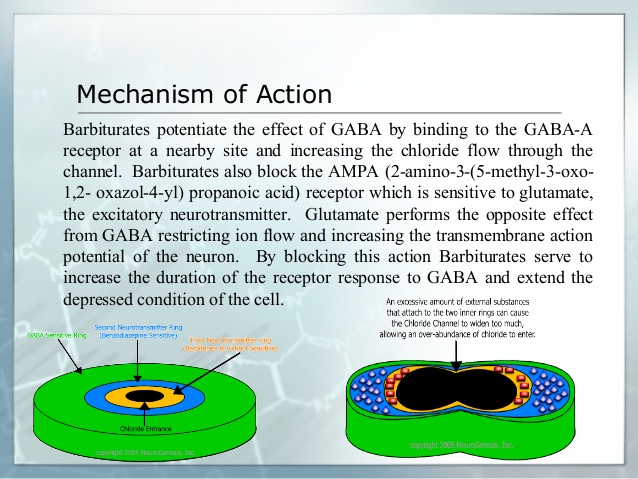
Butalbital exerts a generalized depressant effect on the central nervous system and, in very high doses, has peripheral effects. The acetaminophen in Fioricet is a pain reliever, the caffeine works as a stimulant to increase the acetaminophen’s effectiveness, and the butalbital is a sedative that decreases anxiety while causing relaxation and sleepiness. These actions are believed to ease migraine symptoms, but there is limited evidence that barbituates ease migraine symptoms.
-
- Fioricet is a combination pain-reliever (analgesic) containing acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine.
- Experts aren’t sure exactly how acetaminophen works, but suspect it blocks a specific type of cyclo-oxygenase (COX) enzyme, located mainly in the brain.
- Butalbital belongs to the class of medicines called barbiturates. When used for pain due to tension headaches experts believe it works by relaxing muscle contractions and causing sedation via an enhancement of the inhibitory effects of GABA (a neurotransmitter that regulates communication between brain cells).
- Caffeine is thought to enhance the pain-relieving effects of acetaminophen by up to 40%. In addition, it has vasoconstrictive properties, narrowing blood vessels in the brain thereby decreasing blood flow and oxygen tension (before a headache or a migraine, blood vessels tend to enlarge). This also helps to relieve pain.
- Fioricet belongs to the class of medicines known as barbiturates because it contains butalbital. It may also be called a combination analgesic.
Downsides of Taking Fioricet
If you are between the ages of 18 and 60, take no other medication or have no other medical conditions, side effects you are more likely to experience include:
-
- Dizziness, drowsiness, lightheadedness, sedation, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or an intoxicated feeling are the most commonly reported side effects.
- Other side effects, such as constipation, excessive sweating, itch, serious skin reactions, and mental confusion are less common.
- Taken every four hours as needed but use should not exceed 6 tablets or capsules daily.
- Butalbital is habit-forming and there is a high risk of dependence with extended and repeated use of Fioricet. Therefore it is not considered a first-choice medicine for headaches.
- May cause a medication-overuse headache with repeated use (more than 3 days per month) and a withdrawal syndrome (symptoms include worsened headache, nausea/vomiting, restlessness, anxiety, disturbed sleep, and sweating) upon discontinuation. When stopping acetaminophen/butalbital/caffeine that has been taken long-term, taper the dose down and discontinue slowly over 2 to 4 weeks. If a person has developed chronic migraines, consider replacing Fioricet with phenobarbital and gradually tapering down.
- The potential for liver damage with the acetaminophen component exists, even at recommended dosages. The risk is increased with higher dosages, with chronic alcohol use, with some medications, and in patients with significant liver disease.
- May not be suitable for some people, including the elderly and people with kidney or liver disease.
- Although Fioricet may be prescribed for migraine headaches, it is not FDA-approved for this and the evidence does not support its use for migraine.
- Only available as tablets.
- Should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- May interact with several other medications including those that also cause sedation such as opioids, benzodiazepines, and sedating antihistamines. Alcohol should be avoided.
Signs And Symptoms Of Fioricet Abuse And Addiction
One sign of Fioricet abuse and addiction is needing to take more of the drug to achieve the desired effects, which is called tolerance. Butalbital, a barbiturate ingredient in Fioricet, is likely to cause tolerance after prolonged use of high doses. Taking too much Fioricet may also result in an increase of side effects. Experiencing more side effects may suggest the drug is being abused.
Potential Fioricet side effects may include:
-
-
-
- confusion
- depression
- drowsiness
- lightheadedness
- stomach pain
- trouble sleeping
- upset stomach
-
-
The high from Fioricet may cause someone to appear sleepy, drowsy, and sedated. Even at fairly low doses, barbiturates can make a person seem drunk or intoxicated. They may seem distant or uninterested in activities they usually engage in. Their appearance may change and become more messy and unkempt. Relationships may begin to deteriorate and they may neglect responsibilities at home work or school.
Someone abusing Fioricet may also suffer from barbiturate addiction or dependence. The average barbiturate dose someone needs when suffering from barbiturate addiction is around 1500 mg a day, on average. Butalbital, a barbiturate in Fioricet, consists of only 50 mg. They may be taking multiple large doses of Fioricet, which can be dangerous.
Can You Get Fioricet High?
A Fioricet high and experiences from its use may vary from person to person. The amount of Fioricet taken by a person plays an important role in causing the experience upon intake.
An overdose of Fioricet can get you high enough to feel intensely intoxicated and may result in serious problems leading to death in some cases.
Fioricet Overdose
The overdose of Fioricet is toxic and may quickly lead to liver failure, upper gastrointestinal bleeding, a respiratory breakdown which may subsequently result in death.
Fioricet overdose is slightly perplexed as there are two factors into play, acetaminophen, and butalbital.
The acetaminophen present in Fioricet is a lethal substance if ingested in excessive amounts, but even a low dose of 4,000mg can cause liver damage to the human body. If 10,000 to 15,000 mg of acetaminophen finds a way into your body, it can quickly kill you by way of acute liver failure, acute renal failure or upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
To counter the overdose of acetaminophen, doctors use N-acetylcysteine.
Further to it, the butalbital, which is a type of barbiturate, can contaminate the body swiftly and disrupt the respiratory system causing death within minutes. For butalbital overdose, the doctors do not yet have a precise cure, but procedures such as activated charcoal injection via nose; insertion of glucose, saline, thiamine, etc. are the most common remedies to offset the butalbital overdose reaction.
In the event of an overdose on Fioricet, call 911 immediately. Emergency treatment is critical to ensure the person remains stable. After the immediate overdose risk is averted, subsequent care is essential to effectively address the drug abuse or addiction issue.
Fioricet rehab treatment normally begins with the detoxification phase. This process reduces the patient’s dosage of Fioricet until they are no longer taking the drug at all. The detoxification phase of the treatment eliminates the patient’s physical dependence on Fioricet. The remainder of a treatment program for Fioricet addiction deals primarily with the psychological aspect of the addiction.
Is Fioricet addictive?
Yes, Fioricet can be highly addictive. Fioricet is a combination of acetaminiophen, butalbital, and caffeine. The acetaminophen brings relief from chronic pain and the butalbital acts as a sedative. This combination of chemicals can produce feelings of euphoria, making the drug difficult to give up.
Withdrawal from Butalbital (Present in Fioricet)
As frequently mentioned in the earlier lines, the butalbital is highly addictive and hence Fioricet is a potentially dangerous drug for substance abuse. Once getting hooked on Fioricet, the dependent may feel the need to rely on it in every situation. Its use results in loss of focus, dizziness and impaired decision making.
Many tend to use Fioricet as a substitute for other prescription drugs for getting high. The high you get out of Fioricet might only last for a short period of time but what follows is an absolutely dangerous and life-threatening ordeal.
Being a primary constituent in Fioricet, butalbital is prevalent in teens and adults as a recreational drug. Although Fioricet is not enlisted as a controlled substance in the USA, its variant Fiorinal has Codeine in its composition, due to which Fiorinal is a controlled substance.
It is advised to use Fioricet as a means for medical purposes only. Just like with any other drug, unless you abuse it, Fioricet is a very effective and much commonly prescribed drug by doctors for chronic head pain and migraines.
Signs of an overdose on Fioricet include the following:
-
-
- Anxiety
- Breathing trouble
- Raised blood pressure
- Elevated body temperature
- Delirium
- Tiredness
- Headaches
- Increased heart rate
- Nausea
- Ringing in the ears
- Shaking
-
Does Fioricet Work for Migraine Headaches?
Fioricet (butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine) has been around forever and is used by many for the treatment of chronic migraine or tension headaches. It is a mixture of a barbiturate, Tylenol (acetaminophen) and caffeine.
Now, many formularies are no longer covering Fioricet capsules. For those of you who have relied on it for years, this (understandably) may make you nervous.
Well, it turns out it doesn’t really work that well—and there are much better options out there.
- Fioricet and Fioricet with Codeine are not as effective for acute migraine as newer medications. There isn’t any evidence that shows that barbiturate-containing meds (the butalbital in Fioricet) help for migraine treatment. In fact, the use of Fioricet with Codeine often results in chronic migraine and a “medication overuse headache.”
- NSAIDS. Start with these instead. There is good evidence that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs—ibuprofen, naproxen, and others—work well for the treatment of acute migraine.
- Triptans. Imitrex (sumatriptan), Maxalt (rizatriptan), Relpax (eletriptan), and Frova (frovatriptan) are examples. Used alone or in combination with an NSAID, triptans work well for moderate to severe headaches that aren’t relieved by NSAIDs alone. Wondering which to choose? They generally work the same but you may notice fewer side effects with one over the other. Cost can also be an issue so you’ll want to pick a triptan that is covered by your insurance plan. It’s also a good idea to check GoodRx to see if the cash or discount price beats your co-pay.
- Adding a nausea medication. For folks with moderate to severe migraine accompanied by nausea or vomiting, adding Reglan (metoclopramide) , Zofran (ondansetron) or Compazine (prochlorperazine) also helps.
Bottom line is . . . while your Fioricet capsules may no longer be covered, better options exist.
- What is Fioricet and How to buy Fioricet COD online ?
- Tips of taking Fioricet
- Downside of taking Foricet
- Buy Fioricet Online
- Fioricet Side Effects and Fioricet Interactions with Other Medications
- What is Sinus Headache and How to Treat Sinus Headache ?
- Fioricet Overdose Signs and Symptoms and Treatment
- Esgic Precautions
- Esgic Drug Interactions
- Esgic Description and Brand Names
- How is Esgic Tablets Supplied
- Esgic Over-dosage and Treatment
- Esgic Abuse and Dependence
- Esgic Adverse Reactions
- What is narcotic analgesic apap caffeine butalbital oral ?
- Buy Fioricet and Gabapentin Online
- Butalbital CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Migraine Headache Surgery
- Sinus Headache Remedies
- Headache treatment
We do not suggest you to take Fioricet or Gabapentin for a long time, you need go to your local health professional to treat your pain without prescription. We think exercising is the best way to relieve your pain. Exercising is a very good methods. Exercising can enhance your immune system and increase your muscle strength and make your nerve strong.
You can also take some nutrition from food. Becoming an USANA distributor and taking nutritions will make you much more health than before.
Does Fioricet Cause Weight Loss ?
In clinical studies, weight loss was not a reported side effect from Fioricet. However, it can cause nausea, vomiting and stomach pain. Having those side effects may lead to a decreased appetite and lead to weight loss.
What You Should Know Before Taking Fioricet ?
Do not use this medicine if you have taken an MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days. A dangerous drug interaction could occur. MAO inhibitors include isocarboxazid, linezolid, phenelzine, rasagiline, selegiline, and tranylcypromine.
You should not use acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine if you are allergic to it, if you have porphyria, or if you have recently used alcohol, sedatives, tranquilizers, or other narcotic medications.
To make sure acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have:
-
-
- liver disease, cirrhosis, a history of alcoholism or drug addiction, or if you drink more than 3 alcoholic beverages per day;
- kidney disease;
- asthma, sleep apnea, or other breathing disorder;
- stomach ulcer or bleeding;
- a history of skin rash caused by any medication;
- a history of mental illness or suicidal thoughts; or
- if you use medicine to prevent blood clots.
-
It is not known whether this medicine will harm an unborn baby. If you use butalbital while you are pregnant, your baby could become dependent on the drug. This can cause life-threatening withdrawal symptoms in the baby after it is born. Babies born dependent on habit-forming medicine may need medical treatment for several weeks. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
Fioricet Warnings
Fioricet carries a black-box warning cautioning users about the link of acetaminophen to acute liver failure. In some cases, users of Fioricet have needed a liver transplant; in other cases, use of Fioricet has proven fatal.
Most problems have occurred with an acetaminophen dose of more than 4,000 mg a day. Those affected are often taking more than one product containing acetaminophen at the same time or have underlying liver disease.
Another caution concerns butalbital, which may be habit-forming and therefore has the potential to be abused. Those with a condition known as porphyria, a rare hereditary blood disorder, should not use Fioricet.
Pregnancy and Fioricet
Fioricet is in Pregnancy Category C, according to the FDA, which means that injury to the developing fetus cannot be ruled out. Even so, the benefits of the drug to the mother must be weighed against the potential risk to the unborn baby.
All three drugs found in Fioricet are found in small amounts in human milk, but the significance of that is not known.
You should discuss with your doctor whether to stop breastfeeding or stop taking the drug, weighing the benefits against the costs.
The Fioricet ‘High’ and Abuse
The butalbital in Fioricet belongs to a class of drugs called barbiturates, a central nervous system depressant. Like other barbiturates, it has the potential to cause physical and psychological dependence, which can lead to abuse.
Those who use too much Fioricet may report feeling so relaxed and stress-free that they seek out the drug as a way to get high. Some describe it as feeling intoxicated. However, users can feel depressed and “crash” once the effects wear off.

Fioricet is the best headache reliever and can be used for all kinds of headaches.
Fioricet is the Uncut Gem of headache medicine!